What is high blood pressure? What is normal blood pressure?
- High blood pressure (hypertension) is defined as high pressure (tension) in the arteries, which are the vessels that carry blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
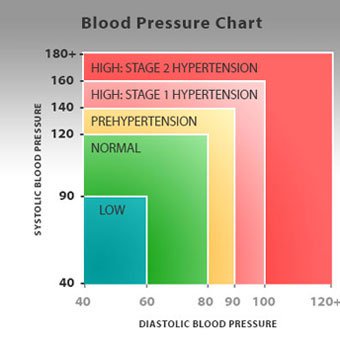
- Blood pressure readings are given as two numbers:
- The systolic blood pressure (the top number) equals the pressure in the arteries as the heart contracts.
- The diastolic pressure (the bottom number) is the pressure in the arteries as the heart relaxes.
- Normal blood pressure is below 120/80.
- In 2017, the American College of Cardiology released new guidelines for high blood pressure.
- Blood pressure between 120/80 and 129/80 is elevated blood pressure, and a blood pressure of 130/80 or above is considered high.
- The American Academy of Cardiology defines blood pressure ranges as:
- Hypertension stage 1 is 130-139 or 80-89 mm Hg, and hypertension stage 2 is 140 or higher, or 90 mm Hg or higher.
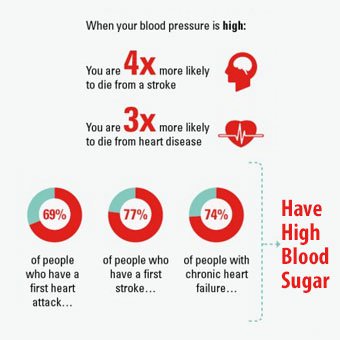
- Complications of high blood pressure include heart disease, kidney (renal) disease, hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis or arteriosclerosis), eye damage, and stroke (brain damage).
- Hypertension is a major public health problem. With the new guidelines for defining high blood presure, The American Heart Association estimates high blood pressure affects nearly half of all adults (46%) in the United States.
High Blood Pressure Treatment
Other dietary considerations
It is beneficial to add potassium to the diet. Studies show that people who consume more potassium have lower blood pressures. Good sources of potassium include:
- bananas,
- melons,
- oranges,
- spinach and
- zucchini.
Along with lowering salt in the diet, a balanced eating plan that also reduces cholesterol intake and fatty foods is recommended. The TLC Diet (Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes) often is recommended to lower blood cholesterol.
What do blood pressure readings mean? (blood pressure readings chart)
Blood pressure readings can vary in a single person throughout the day depending on the situation. Factors such as stress, anxiety, foods eaten (caffeine or salt intake), smoking, or exercise can cause pressure to rise.
The American Heart Association defines a normal blood pressure as less than 120/80. Elevated blood pressure ranges between 120/80 and 129/80, and high blood pressure is 130/80 and higher. In pregnancy normal blood pressure should be below 120/80.
If your blood pressure reaches into the high range, you should see your doctor about lifestyle changes, and possibly medication especially if you have other risk factors, such as diabetes or heart disease.
High blood pressure (for example, 180/110 or higher) may indicate an emergency situation. If this high blood pressure is associated with chest pain, shortness of breath, headache, dizziness, or back or abdominal pain, seek medical care immediately. If you are experiencing no associated symptoms with a high blood pressure reading such as this, re-check it again within a few minutes and contact your doctor or go to an emergency room if it is still high.
If your blood pressure is lower than about 100/60 you may have low blood pressure, depending on the associated symptoms. If you are unsure, check with your doctor.
What are the signs and symptoms of high blood pressure?
High blood pressure may not have any symptoms and so hypertension has been labeled "the silent killer." Longstanding high blood pressure can lead to multiple complications including heart attack, kidney disease, or stroke.
Some people experience symptoms with their high blood pressure. These symptoms include:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Blurred vision
- Feeling of pulsations in the neck or head
- Nausea
What causes high blood pressure?
The causes of hypertension are multifactorial, meaning there are several factors whose combined effects produce hypertension.
- High salt intake or salt sensitivity: This occurs in certain populations such as the elderly, African Americans, people who are obese, or people with kidney (renal) problems.
- Genetic predisposition to high blood pressure: People who have one or two parents with hypertension have high blood pressure incidence about twice as high as the general population.
- A particular abnormality of the arteries, which results in an increased resistance (stiffness or lack of elasticity) in the tiny arteries (arterioles): This increased peripheral arteriolar stiffness develops in individuals who are also obese, do not exercise, have high salt intake, and are older.
How is blood pressure measured?
Blood pressure is measured by a blood pressure cuff (sphygmomanometer). The blood pressure cuff consists of an air pump, a pressure gauge, and a rubber cuff. The instrument measures the blood pressure in units called millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
The cuff is placed around the upper arm and inflated with an air pump to a pressure that blocks the flow of blood in the main artery that travels through the arm. The arm is held at the side of the body at the level of the heart, and the pressure of the cuff is gradually released. As the pressure decreases, a health practitioner listens with a stethoscope over the artery at the front of the elbow or an electronic machine senses the pulsation. The pressure at which the practitioner (or machine) first hears a pulsation from the artery is the systolic pressure (the top number). As the cuff pressure decreases further, the pressure at which the pulsation finally stops is the diastolic pressure (the bottom number).
How is high blood pressure diagnosed?
To make an official diagnosis of high blood pressure you will need to see your doctor. Often your blood pressure will be checked on at least two different visits, at different times of the day. Your doctor may ask you to keep a blood pressure log for a short time in order to see your overall blood pressure trends. If your blood pressure is consistently over 134/80, your doctor will work with you to determine the best regimen for treating your high blood pressure.
What is the treatment for high blood pressure?
Blood pressure is caused by many different factors, so there are many different treatments. The goal of treating high blood pressure is to keep the blood pressure below 134/80.
Treatments for high blood pressure include:
- Lifestyle modifications:
- Quit smoking
- Lose weight if you are overweight
- Exercise
- Avoid alcohol
- Eat a low-sodium, low-fat diet like the DASH diet.
- Medications: There are many different categories of blood pressure medications. Your doctor will work with you to find the right one. The main types include:
- Beta blockers
- Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
- Angiotensin II Receptor (ARB) blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Diuretics (water pills)
- Treatment of underlying conditions that cause high blood pressure, such as:
What changes in diet help lower blood pressure naturally?
Dietary changes are often the first line of treatment recommended by your doctor. You may be advised to:
- Limit caffeine intake
- Reduce salt intake
- Limit fatty foods
- Avoid alcohol
- Manage cholesterol
- Add potassium-rich foods to your diet (unless you are being treated for kidney failure, as potassium rich foods may be harmful to you)
Doctors often recommend the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) Diet created by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI), which focuses on whole grains, fruits and vegetables, low-fat dairy, and lean meats.
In addition to dietary modification, quitting smoking is extremely beneficial in managing high blood pressure.
Dietary changes are often the first line of treatment recommended by your doctor. You may be advised to:
- Limit caffeine intake
- Reduce salt intake
- Limit fatty foods
- Avoid alcohol
- Manage cholesterol
- Add potassium-rich foods to your diet (unless you are being treated for kidney failure, as potassium rich foods may be harmful to you)
Doctors often recommend the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) Diet created by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI), which focuses on whole grains, fruits and vegetables, low-fat dairy, and lean meats.
In addition to dietary modification, quitting smoking is extremely beneficial in managing high blood pressure.Can exercise help lower high blood pressure?
Exercise and physical activity helps lower blood pressure by helping you lose weight and keeping your heart and blood vessels in good condition.
Weight loss achieved through diet and exercise helps control factors such as blood sugar, and other complications of obesity. Avoiding these complications helps lower blood pressure and prevent high blood pressure.
Consult your doctor before starting any new exercise program. Cardiovascular activities including walking, jogging, biking, or swimming for 30 to 45 minutes per day can help lower blood pressure.
What alternative therapies help lower and mangage high blood pressure?
Some complementary and alternative medicine strategies can help you manage your high blood pressure and prevent it from becoming elevated further.
- Reduce stress.
- Use relaxation methods such as deep breathing, imagery relaxation, yoga, meditation, and biofeedback.
- Keep a daily blood pressure chart.
- Get adequate sleep.
- Some home remedies, such as garlic, coenzyme Q-10 (CoQ10), calcium, magnesium, fish oil, and flaxseed have been shown in studies to lower blood pressure. Consult your physician before taking any supplements.
What alternative therapies help lower and mangage high blood pressure?
Some complementary and alternative medicine strategies can help you manage your high blood pressure and prevent it from becoming elevated further.
- Reduce stress.
- Use relaxation methods such as deep breathing, imagery relaxation, yoga, meditation, and biofeedback.
- Keep a daily blood pressure chart.
- Get adequate sleep.
- Some home remedies, such as garlic, coenzyme Q-10 (CoQ10), calcium, magnesium, fish oil, and flaxseed have been shown in studies to lower blood pressure. Consult your physician before taking any supplements.
source:MedicineNet.com



